Charsire New Drug CSTC1 for
DIABETIC FOOT ULCER
Beneficial to chronic ulcer wounds

Toxicology tests for phase II and phase III, completed

Phase II clinical study approved by US FDA, ongoing
Overview & Medication Predicament::
Long Healing Period &
High Risk of Infection
Peripheral microvascular problems in diabetes are often accompanied by peripheral vascular occlusion, resulting in wounds on extremities being difficult to heal, and increasing the chance of infection. Also, the functions of white blood cells and lymphocytes in diabetic patients are worse than a normal person; therefore, the affected tissue is prone to become necrotic once the wound is infected.
Wound occurs – Slow wound healing – Inflammation & Infection – Slow down revascularization – Slow wound healing – Repeated inflammation & infection. Wound care becomes extremely difficult in this repeated situation.
Current topical care of chronic ulcer wounds employs tissue regeneration technologies to culture autologous regenerative factors and reinject back to help wound repair and regeneration. However, these treatments are usually costly. Although oral drugs can control infection, wound healing and reconstruction occur slowly. Currently, there is no safe and effective wound medication for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers.
Core Technology of CSTC1
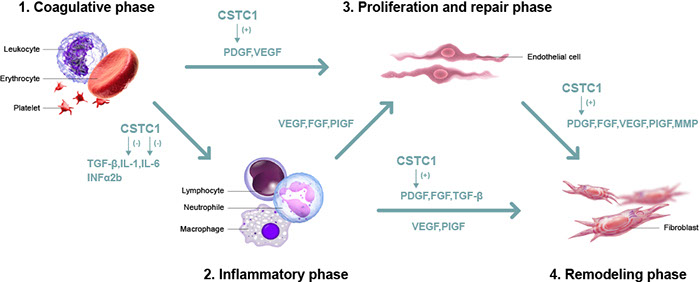
Diabetic foot ulcer new drug (CSTC1) facilitates diabetic wound healing by reducing IL-1β at inflammatory phase and increasing PDGF at proliferative phase. Thus, CSTC1 can shorten the inflammatory phase, accelerate the revascularization phase, and improve cell reorganization (to help wound healing).
Meet Medical Needs
In 2017, there was 150 million diabetic patients worldwide, and 64 million diabetic patients had diabetic foot ulcer problems. Diabetic foot ulcer occurs in 15% of all diabetic patients, 84% of these patients will face amputation. A growing need for medical wound care drove the market value of wound dressing to 21.6 billion US dollars.
CSTC1 Applications
In addition to diabetic foot ulcer wounds, CSTC1 can be used for chronic wounds caused by hypertension, chronic diseases, renal problems, cardiovascular problems, and acne due to poor microvascular circulations (often occurring in prolonged bed rest). CSTC1 can effectively benefit ulcer wound care.
